How to operate a drone effectively and safely is a topic that blends technological prowess with responsible operation. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone flight, from understanding the fundamental components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll explore everything from basic controls and camera operation to troubleshooting common issues and maintaining your drone for optimal performance and longevity.
Prepare to take flight with confidence and knowledge.
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to learning how to operate a drone, covering everything from pre-flight preparations to advanced flight techniques. We will break down complex concepts into easily digestible segments, equipping you with the skills and knowledge necessary for safe and successful drone operation.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts, their functions, and potential issues you might encounter.
Major Drone Components
| Component Name | Function | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Provide thrust and lift, enabling flight. | Damage from impacts, imbalance leading to vibrations, or wear and tear requiring replacement. |
| Motors | Spin the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. | Motor burnout due to overheating or excessive load, malfunction due to water damage or impact. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, processing data from sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions (gyro, accelerometer), damage from impacts affecting its functionality. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Overheating, depletion, damage from impacts or improper charging, reduced capacity over time. |
| GPS | Provides location data for navigation and autonomous flight modes. | Weak signal in areas with poor GPS reception (e.g., dense urban areas or indoors), interference affecting accuracy. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos. | Lens damage, malfunctioning sensor, image distortion, poor image quality due to improper settings. |
Drone Battery Types and Performance, How to operate a drone
Different drone batteries offer varying flight times and performance characteristics. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the most common type, known for their high energy density. However, they require careful handling due to their flammability. Factors such as battery capacity (mAh), voltage (V), and C-rating (discharge rate) significantly influence flight time and power output. Higher mAh means longer flight time, higher voltage implies more power, and a higher C-rating allows for faster discharge, crucial for more demanding flight maneuvers.
Flight Controller Functionality
The flight controller is the central processing unit of the drone, integrating data from various sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes, and barometers to maintain stability and execute pilot commands. It receives input from the remote controller and adjusts the motor speeds individually to achieve the desired flight behavior. Furthermore, the flight controller interacts with the GPS module for position holding and autonomous flight modes, ensuring precise and controlled movements.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight inspection is paramount for safe drone operation. Neglecting this crucial step can lead to accidents and equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Visually inspect the drone for any physical damage (propeller cracks, loose parts, etc.).
- Check the battery level and ensure it is properly connected.
- Verify the connection between the drone and the remote controller.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS (detailed below).
- Confirm that all necessary software updates are installed.
- Check the surrounding environment for any potential hazards (obstacles, people, etc.).
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the compass and GPS ensures accurate navigation and stable flight. The compass calibration process usually involves rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern while the GPS calibration involves letting the drone sit still for several minutes to acquire a strong signal. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior and loss of position.
Safe Battery Charging and Storage
Always charge LiPo batteries in a fire-resistant environment and never leave them unattended during charging. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Overcharging or discharging can damage the battery, reducing its lifespan and posing a fire hazard. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storage.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. These procedures vary depending on the environment.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Open Field Takeoff and Landing
- Ensure a clear, open space with no obstacles.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off vertically.
- Maintain a stable hover before proceeding with flight.
- For landing, slowly descend vertically and gently reduce throttle to a complete stop.
Urban Area Takeoff and Landing
- Choose a location away from buildings, crowds, and power lines.
- Be mindful of airspace restrictions.
- Perform a thorough pre-flight check.
- Takeoff and land slowly and smoothly to avoid sudden movements.
- Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
Wind Conditions
Strong winds can significantly impact takeoff and landing. In windy conditions, it’s essential to choose a sheltered location and adjust the drone’s orientation to minimize the effect of wind gusts. It might be necessary to postpone flight until conditions improve.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In case of an emergency, prioritize a safe landing. If the drone loses control, attempt to bring it down in a clear, open area, away from people and obstacles. Many drones have a “return to home” function that can automatically guide the drone back to its takeoff point. Familiarize yourself with this function before flying.
Basic Drone Flight Controls
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section explains the function of the control sticks and flight modes.
Control Stick Functions
Most drone controllers use two joysticks: the left stick controls altitude and yaw, and the right stick controls pitch and roll.
- Throttle (left stick, up/down): Controls the drone’s altitude. Pushing up increases altitude, pushing down decreases it.
- Yaw (left stick, left/right): Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis. Pushing left rotates counter-clockwise, pushing right rotates clockwise.
- Pitch (right stick, forward/backward): Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward. Pushing forward moves the drone forward, pushing backward moves it backward.
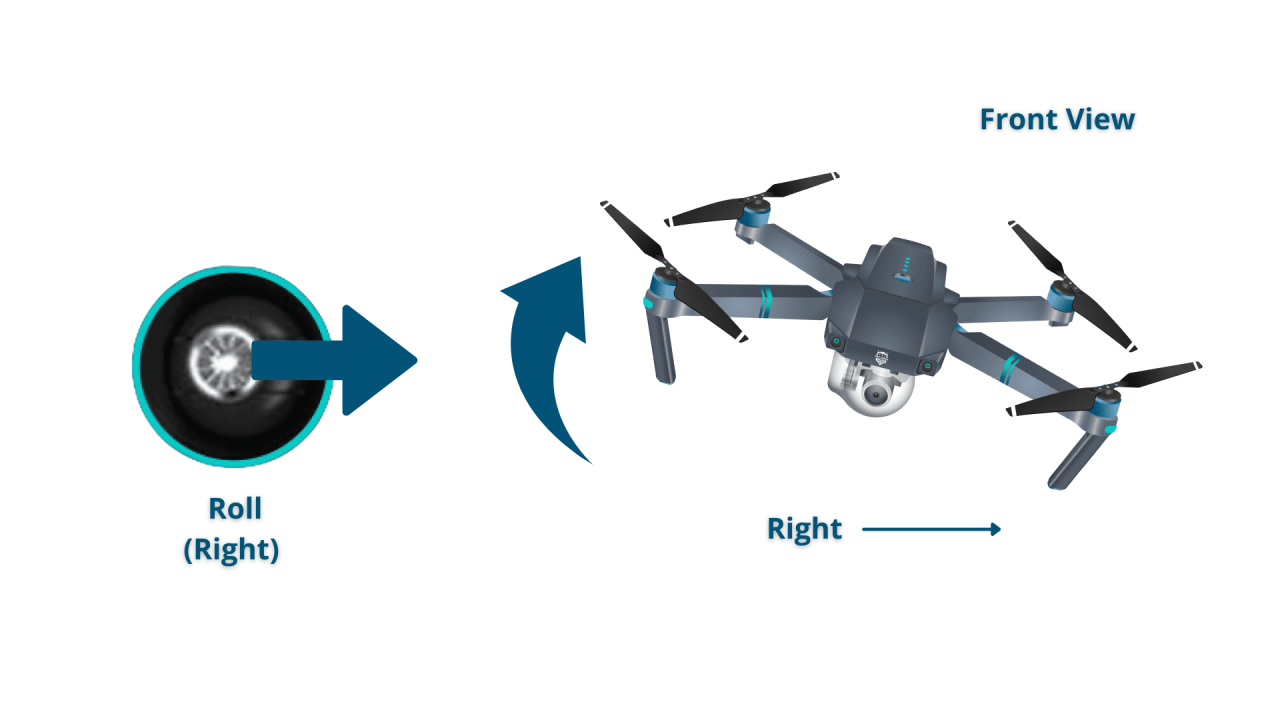
- Roll (right stick, left/right): Controls the drone’s movement left and right. Pushing left tilts the drone to the left, pushing right tilts it to the right.
Altitude Hold
Altitude hold is a crucial feature that maintains a constant altitude, simplifying flight and reducing the risk of crashes. It uses sensors to detect altitude changes and automatically adjusts the throttle to compensate.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight situations. Beginner modes often limit speed and responsiveness, while advanced modes offer greater control and maneuverability. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each mode is crucial for safe operation.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Optimizing camera settings is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Camera Settings Adjustment
| Setting | Function | Effect on Image Quality | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | Determines the image size (e.g., 1080p, 4K). | Higher resolution results in larger file sizes and more detail, but requires more storage space. | Choose the resolution that best suits your needs and storage capacity. |
| ISO | Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. | Higher ISO values allow for shooting in low light, but can introduce noise (grain) into the image. | Balance ISO with shutter speed to achieve the desired image quality. |
| Shutter Speed | Controls the length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. | Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur. | Adjust shutter speed based on the subject’s movement and lighting conditions. |
Camera Angles and Uses
Different camera angles provide unique perspectives and can significantly impact the visual appeal of your aerial shots. High-angle shots offer a broad overview, while low-angle shots provide a dramatic perspective. Side angles can emphasize the subject’s details, and following shots create dynamic and engaging visuals.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots

Effective composition involves carefully considering the placement of the subject within the frame, using the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing images. Experiment with different angles, perspectives, and lighting conditions to achieve the desired effect.
Flight Safety and Regulations: How To Operate A Drone
Adhering to safety regulations and guidelines is essential for responsible drone operation. This section Artikels key safety considerations and regulations.
Safety Regulations and Guidelines
Drone regulations vary by country and region. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. These regulations often include restrictions on flight altitude, distance from airports, and flight over populated areas. Registering your drone with the relevant authorities might also be required.
Safe Distance from People and Obstacles
Always maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles. Avoid flying over crowds or near buildings, power lines, or other hazards. Many drones are equipped with obstacle avoidance systems, but relying solely on these systems is not advisable.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation
- Loss of control: Regularly check the battery level, ensure proper calibration, and be prepared for unexpected events.
- Collisions: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people, and be aware of your surroundings.
- Battery failure: Use high-quality batteries, charge them properly, and always have a spare battery available.
- GPS signal loss: Fly in areas with good GPS reception, and be prepared to land manually if necessary.
- Weather conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common drone problems and provides solutions.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Low battery warnings: Land immediately and charge the battery.
- GPS signal loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception or land the drone.
- Motor malfunctions: Inspect the motors for damage and replace them if necessary.
- Propeller damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Camera issues: Check the camera settings and ensure the lens is clean.
Connectivity Issues
If you experience connectivity issues between the drone and the remote controller, first check the batteries in both devices and ensure they are fully charged. Verify that the frequency channels are correctly matched and that there is no interference from other electronic devices. Restarting both the drone and the remote controller can also resolve connectivity problems. If the issue persists, refer to the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
If your drone crashes, assess the damage and prioritize safety. Carefully inspect the drone for any damage to the frame, propellers, motors, or electronics. If the damage is minor, repairs might be possible. For significant damage, professional repair or replacement might be necessary. Always prioritize your safety during the recovery process.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
This section explores more advanced flight techniques.
Basic Maneuvers
Orbiting a subject involves maintaining a constant distance while circling around it, creating dynamic and engaging footage. Following a pre-planned path requires using waypoint navigation or other autonomous flight modes, allowing for precise and repeatable movements.
Smooth and Stable Aerial Footage

Achieving smooth and stable aerial footage requires practice and mastering the flight controls. Smooth movements are essential for avoiding jerky or shaky footage. Using features like gimbal stabilization and employing slow, deliberate movements contribute significantly to achieving high-quality footage.
Advanced Flight Modes
Waypoint navigation allows you to program a flight path in advance, enabling the drone to automatically follow a pre-defined route. Other advanced flight modes, such as follow-me and point-of-interest, offer additional creative possibilities.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge, and a great resource for learning is available at how to operate a drone. This website offers comprehensive guidance on various aspects of drone operation, ultimately helping you become a confident and responsible drone pilot.
Safe and proficient drone operation is key to responsible use of this technology.
Maintenance Schedule
- Clean the drone regularly: Remove dirt, dust, and debris from the propellers, motors, and body.
- Inspect the drone after each flight: Check for any damage to the propellers, motors, or body.
- Tighten any loose screws or parts: Ensure that all components are securely fastened.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place: Protect it from extreme temperatures and moisture.
Battery Storage
Store LiPo batteries at a partially charged state (around 30-50%) in a cool, dry, and fire-resistant container. Avoid storing them fully charged or fully discharged, as this can shorten their lifespan and increase the risk of fire.
Software Updates
Regularly check for and install software updates. These updates often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features that can enhance the drone’s functionality and safety.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge and practical skills to confidently navigate the skies. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. Embrace the thrill of aerial exploration responsibly, and always prioritize safety above all else. Happy flying!
FAQ Overview
What type of license or registration do I need to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements regarding drone registration and licensing.
How do I ensure my drone’s GPS signal is strong?
Fly in open areas with clear visibility to the sky. Avoid obstructions like buildings and trees that may interfere with the GPS signal. Ensure your drone’s firmware is up-to-date.
What should I do if my drone loses connection with the controller?
Most drones have a “return to home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, attempt to regain connection. If still unsuccessful, visually locate the drone and attempt a manual landing if it is safe to do so.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques. Ultimately, mastering how to operate a drone takes practice and a commitment to safety.
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What is the best way to clean my drone after a flight?
Use a soft brush or microfiber cloth to gently remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners. Pay particular attention to the propellers and camera lens.
